The maestro or conductor directs a musical performance involving simultaneous performances of several players or singers using gestures to produce harmonious symphonies. DBA (Database Bandwidth Assignment) is a mechanism in the GPON (Gigabit Passive Optical Network) network that plays the role of a maestro and, using bandwidth maps, distributes, synchronizes, and manages shared upstream bandwidth based on demand, fair distribution, and user bandwidth configurations. Other cable and telecommunication networks like DOCSIS (Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification) and WiMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) also implement mechanisms for Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation.
In the GPON world, DBA is the process by which an OLT (Optical Line Terminal) distributes and reallocates the upstream transmission opportunities to traffic-bearing entities in ONUs (Optical Network Unit) based on the dynamic indication of their activity status and configured traffic contracts. Activity status indication can be through buffer status reporting or transmission of idle GEM (GPON Encapsulation Method) frames in place of granted upstream transmission opportunities. DBA improves upstream bandwidth utilization by reacting adaptively to ONUs’ burst traffic patterns.
The benefits of DBA include:
- Improved upstream resource utilization efficiency
- More subscribers can be supported
- Enhanced services for subscribers
- More flexible SLAs (Service Level Agreements)
PON DBA Abstraction
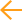
The OLT grants upstream transmission opportunities or upstream bandwidth allocations, to the traffic-bearing entities within the subtending ONUs. These traffic-bearing entities are identified by their Alloc-IDs (Allocation Identifiers). For each Alloc-ID, the logical buffer DBA function module in OLT infers occupancy information by collecting in-band status reports or observing upstream idle pattern. It then provides input to the upstream scheduler that is responsible for generating bandwidth maps. Bandwidth maps are communicated to ONUs in-band with downstream traffic.
DBA Methods
Depending on ONU buffer occupancy inference mechanism, DBA methods can be:
- SR (Status Reporting) DBA → Based on explicit buffer occupancy reports that are solicited by OLT and submitted by ONUs in response
- TM (Traffic Monitoring) DBA → Based on OLTs observation of idle GEM frame patterns and its comparison with the corresponding bandwidth maps
The OLT must support and be capable of accommodating, on the same PON, a mix of SR & TM ONUs.
Mathematical Model of DBA
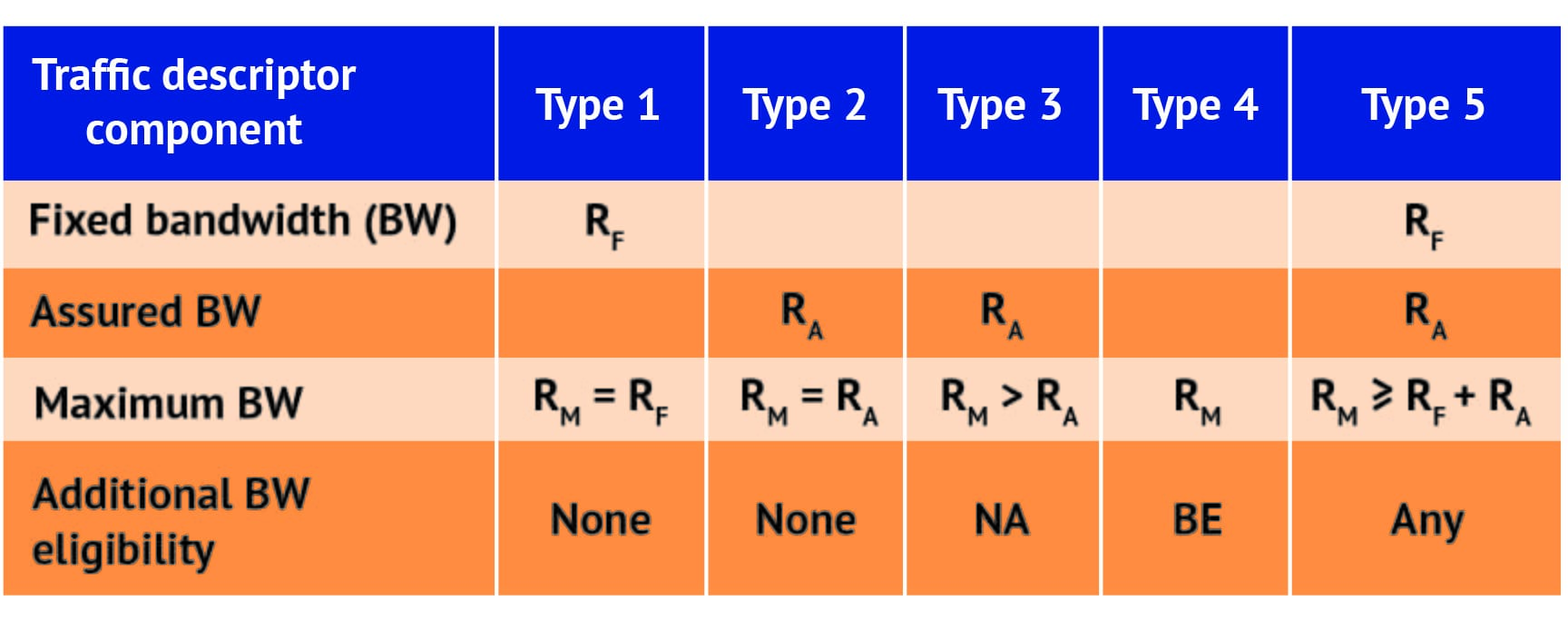
This figure illustrates variants of bandwidth assignment for different offered loads. The prioritization of assigned bandwidth components is as follows, starting with the highest priority and ending in the lowest priority:
- Fixed bandwidth
- Assured bandwidth
- Non-assured bandwidth
- Best-effort bandwidth
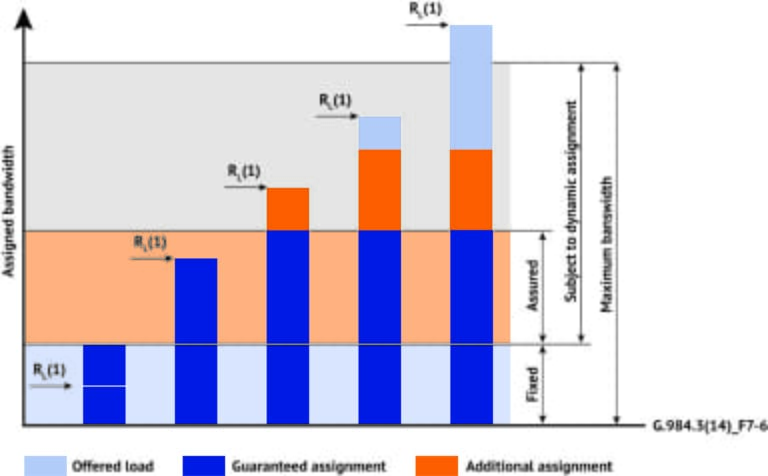
Each of these bandwidth components has specific fairness criteria defined.
The Extended Bandwidth assignment model uses the Extended traffic descriptor for the Best Effort, which includes best-effort priority and weight.
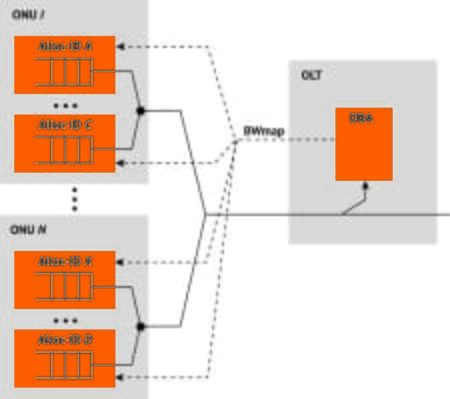
Alloc-ID, Traffic Descriptor, and T-CONT types
T-CONT (Transmission Container) is a traffic bearing object in an ONU representing a group of logical connections and treated as a single entity for the purpose of upstream bandwidth assignment. In general, the bandwidth and eligibility components of the Alloc-ID traffic descriptor for the five types of T-CONT have different relationships with each other, as shown in the table above.
Conclusion
OLT DBA performance is measured using parameters like stationary bandwidth assignment, assured bandwidth restoration time, and DBA convergence time.
This was a quick primer on the intricacies involved in generating the harmonious symphony of efficient, maximal upstream bandwidth using DBA, detailed in standard G984.3. Over the years, working closely with our partners, IP Infusion has developed the expertise in GPON-TC and DBA to help customers bring products to market in the field of GPON, XGPON, and XGSPON.